Self-Preference Your Way In Here
This week: Self-preferencing, a handy ChatGPT chart, exporting dictatorship tools, and brain dynamics
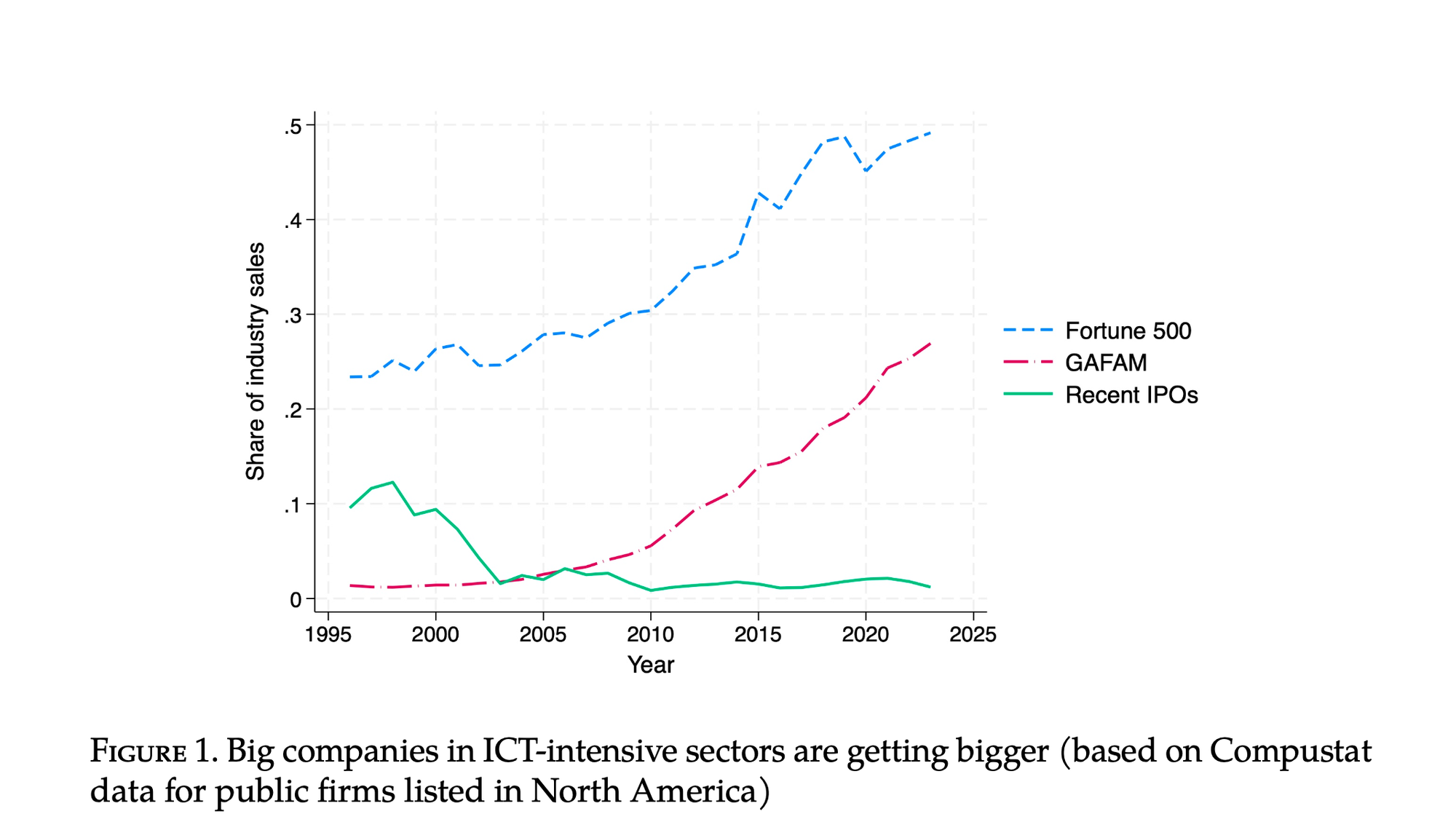
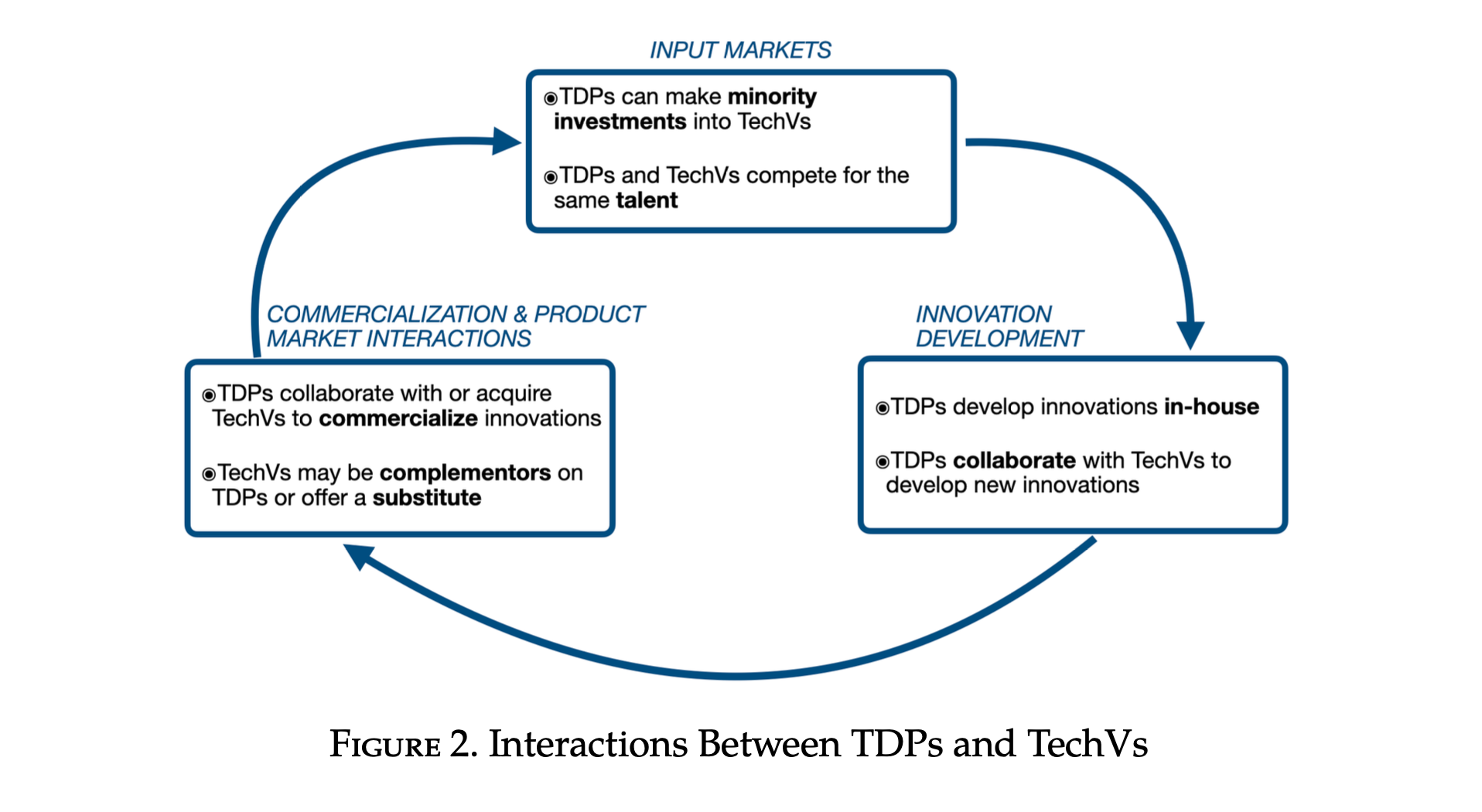
The Role of Digital Platforms in Shaping Tech Venture Innovation
It isn’t just free-riding, it’s self-preferencing!(TM)
“This chapter provides a review of a wide range of interactions between top digital platforms (TDPs) and technology ventures (TechVs), and the corresponding cross-disciplinary literature, highlighting a number of ways in which these relationships can influence the development and diffusion of innovation.”
“As researchers and policymakers search for a principled way to define, detect, and analyze self-preferencing, a few fundamental questions arise. First, since most TDPs are for-profit platforms and have a fiduciary duty to their shareholders, arguably every business decision made by TDPs can have a more favorable impact on the profitability of the platform itself than on third-party sellers on it. How to classify which self-interested TDP decisions meet or do not meet the definition of self-preferencing is still an open question. Second, the welfare standard that should be applied to potential self- preferencing behavior—should the objective be the welfare of final consumers only, the welfare of final consumers and third-party sellers, or the welfare of all platform users plus the profits of the TDP in question—is also an open question. A third open line of inquiry is the extent to which the aforementioned two questions should apply to a small set of select TDPs rather than to all digital platforms or all technology ventures.”
“Theorists also highlight a few costs of R&D alliances. For example, partners may free- ride each other’s R&D efforts because the success of R&D is uncertain, and the benefits of R&D outcomes accrue to all partners, whereas effort costs are private (Bonatti and Hörner 2011). Another cost could originate from a lack of communication. Though the free-riding incentive can be exacerbated by a lack of communication among R&D partners, Campbell, Ederer and Spinnewijn (2014) show that setting an optimal deadline on a research project can help overcome both problems. While free-riding and lack of communication may arise regardless of whether R&D collaboration is inside one firm or across firms, they can be more severe when an R&D alliance involves multiple firms, especially if these firms have conflicting interests in technology transfer and the final product market.”
“Motivated by the trade-offs surrounding the acquisitions of TechVs, Letina, Schmutzler and Seibel (2024) examine the impact of stronger antitrust enforcement within a model where both an incumbent and an entrant pursue innovation, selecting from various available projects. The firms’ strategic choices influence not only their likelihood of innovating but also the degree of correlation between their innovation outcomes and those of their competitors. They find that prohibiting all acquisitions has a weakly negative effect on overall innovation.”
Jin, G. Z., Leccese, M., & Wagman, L. (2025). The Role of Digital Platforms in Shaping Tech Venture Innovation (No. w33370). National Bureau of Economic Research.
https://www.nber.org/papers/w33370
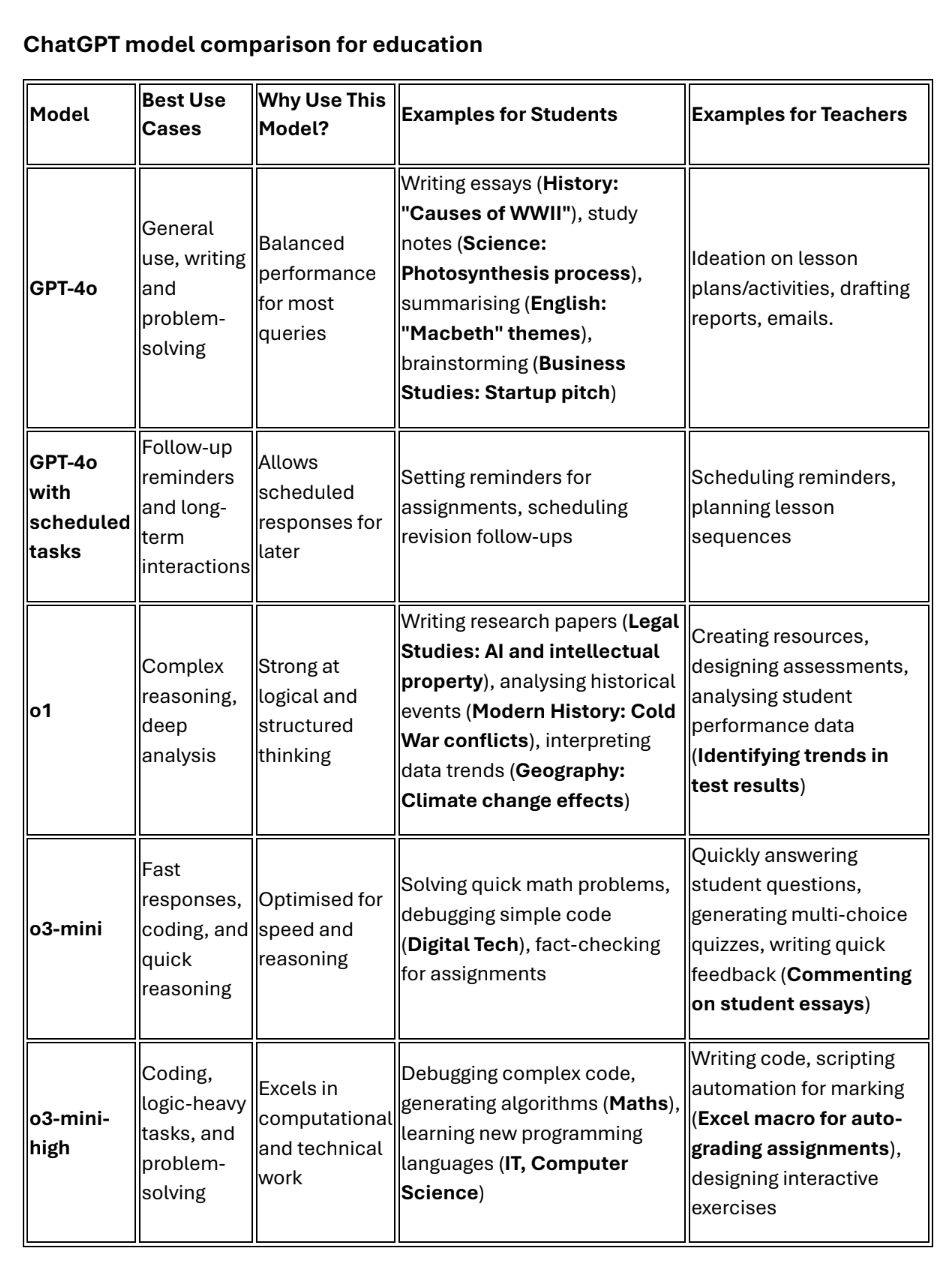
ChatGPT Model for Comparison for Education
Hi Doctor Nick!
Dr. Nick Jackson
https://bsky.app/profile/drnickjackson.bsky.social
Exporting the Tools of Dictatorship: The Politics of China’s Technology Transfers
Demand-Driven Dictatorship
“The Chinese government has revolutionized digital repression at home and is exporting its technologies abroad. These transfers have sparked widespread concern among observers. These tools of digital dictatorship, many argue, will let recipient governments expand surveillance and reinforce the wave of autocratic retrenchment and democratic erosion currently underway. This article presents the first cross-country, plausibly causal evidence that these concerns are justified, but adds nuance.”
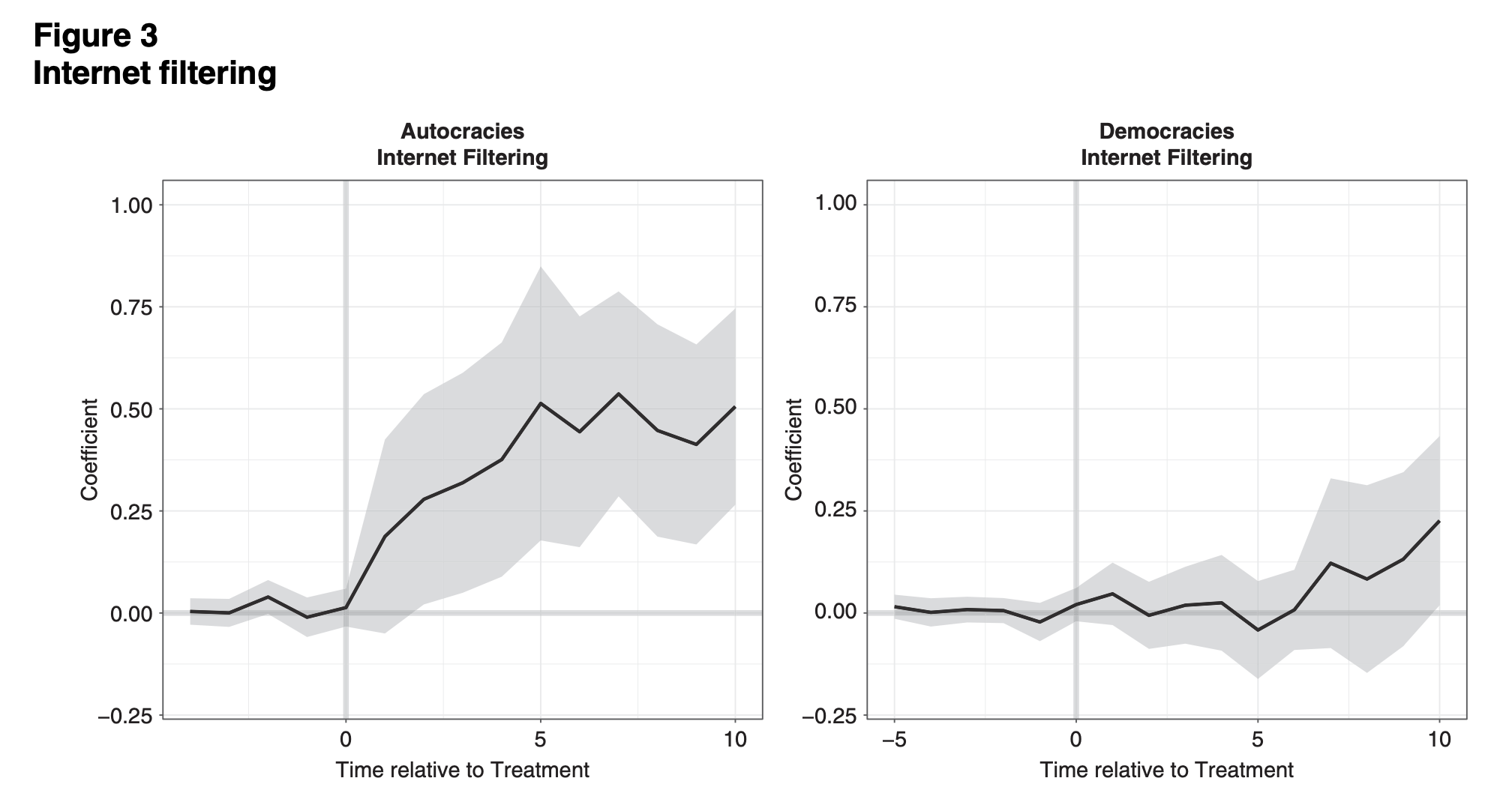
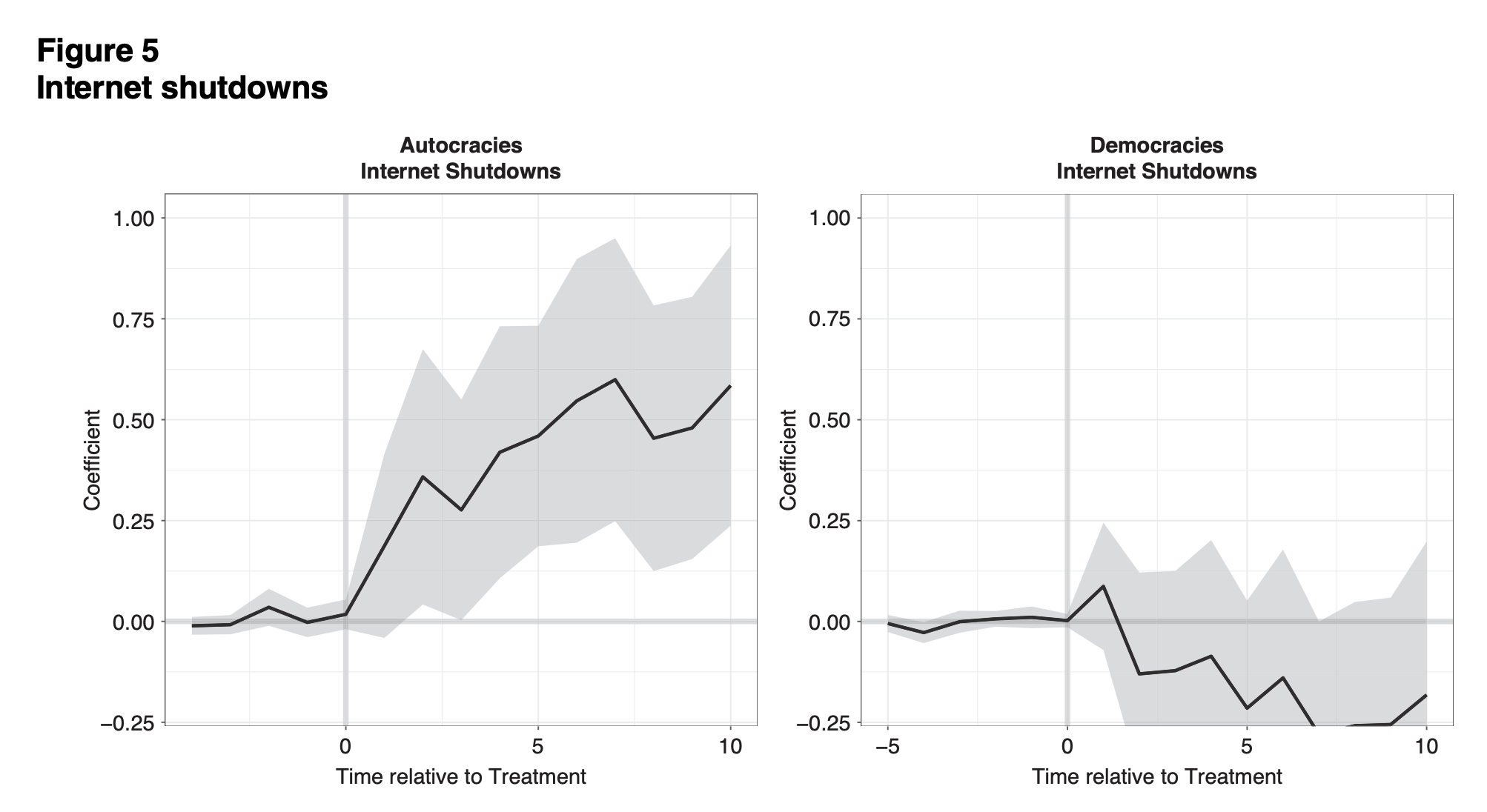
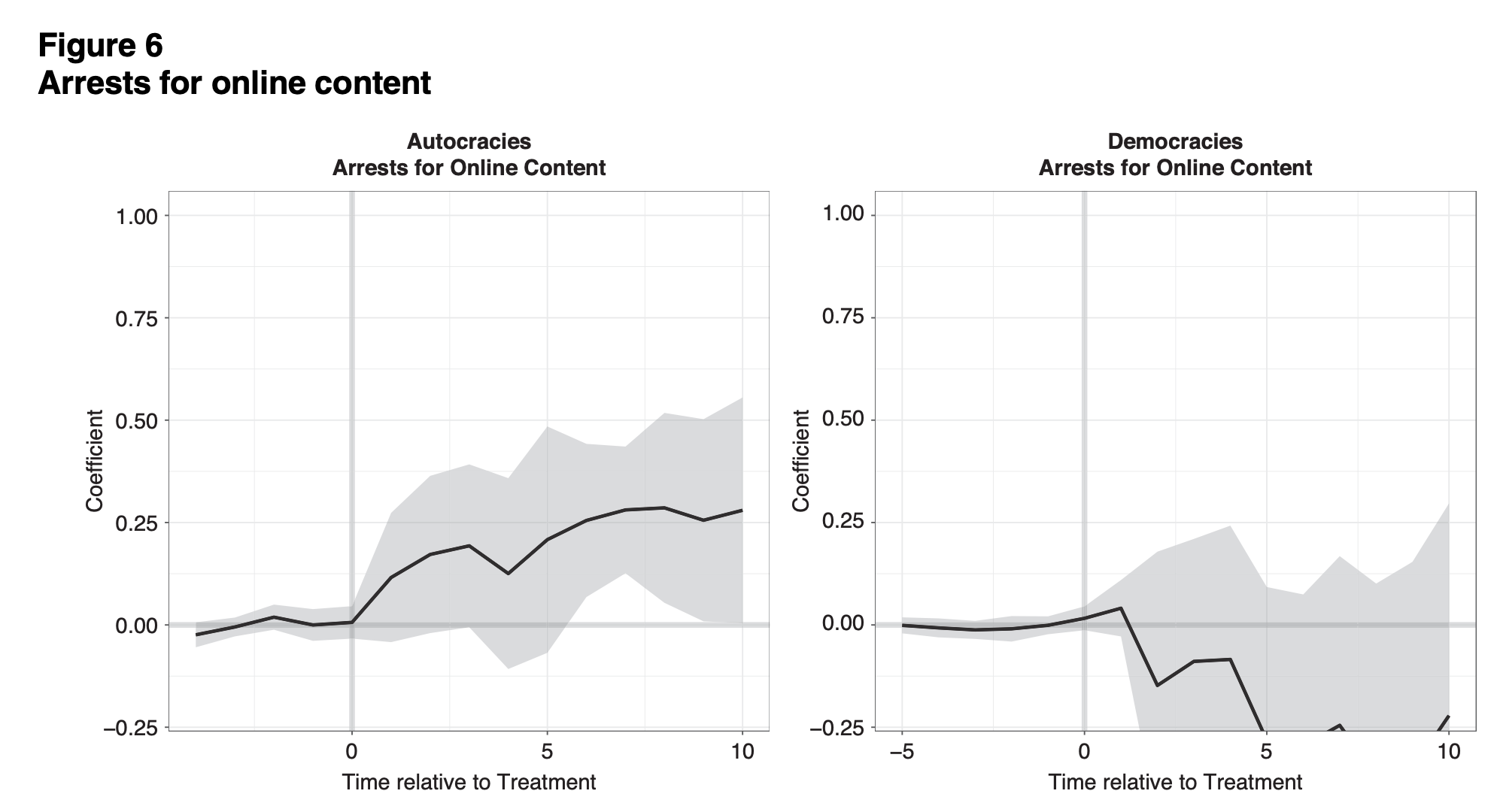
“Huawei transfers are driven chiefly by demand in recipient countries.”
“Third, Huawei’s secrecy means that we also lack fine-grained data about what its transfers entail. Consequently, we cannot ascertain whether certain provisions within contracts are more likely to facilitate digital repression than others. This is almost certainly the case. Transfers that entail “Safe City” infrastructure, for instance, are almost certainly more likely to facilitate digital repression than contracts that focus on IT training for university students.”
Carter, E. B., & Carter, B. L. (2025). Exporting the Tools of Dictatorship: The Politics of China’s Technology Transfers. Perspectives on Politics, 1-20.
Interacting spiral wave patterns underlie complex brain dynamics and are related to cognitive processing
Spriral waves everywhere, all the time.
“Here by characterizing moment-by-moment fluctuations of human cortical functional magnetic resonance imaging signals, we show that spiral-like, rotational wave patterns (brain spirals) are widespread during both resting and cognitive task states. These brain spirals propagate across the cortex while rotating around their phase singularity centres, giving rise to spatiotemporal activity dynamics with non-stationary features. The properties of these brain spirals, such as their rotational directions and locations, are task relevant and can be used to classify different cognitive tasks. We also demonstrate that multiple, interacting brain spirals are involved in coordinating the correlated activations and de-activations of distributed functional regions; this mechanism enables flexible reconfiguration of task-driven activity flow between bottom-up and top-down directions during cognitive processing. Our findings suggest that brain spirals organize complex spatiotemporal dynamics of the human brain and have functional correlates to cognitive processing.”
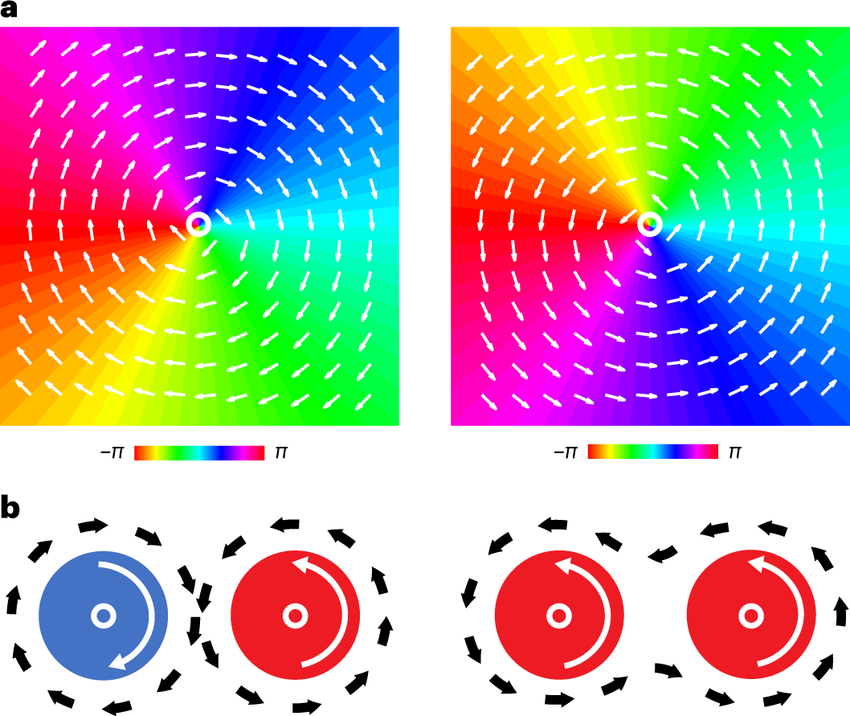
“Schematic illustration of spiral-like, rotational wave patterns and their interactions a, Clockwise (left) and anticlockwise (right) rotating spirals. As detailed in Results, these spirals are characterized by their phase fields (colour map) and the corresponding phase vector fields (phase gradient velocity field, denoted by the white arrows). The radial colour scheme represents phase values. The white circles denote the phase singularities (spiral centres) where all phases converge. b, Pairs of brain spirals with the opposite (left) and same rotational directions (right). The blue and red circles represent the spirals of clockwise and anticlockwise rotating directions, respectively. The white solid arrows represent spiral rotation directions. The black dotted lines with arrows illustrate how activity flows around the spiral pairs.”
Xu, Y., Long, X., Feng, J., & Gong, P. (2023). Interacting spiral wave patterns underlie complex brain dynamics and are related to cognitive processing. Nature human behaviour, 7(7), 1196-1215.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41562-023-01626-5
Reader Feedback
“Yeah, but how much of it [AI adoption] is stealth though?”
Footnotes
See, there’s always a reason why a problem persists. There’s a blocker, a rate limiter, a hurdle, something, that limits the solution of unleashing the potential. This belief is tied up in the idea of efficient markets and the optimism that there are still more mysteries to solve and lots of amazing ideas that society is just not ready to absorb yet. This idea, taken to its extreme, is the franc note meme:
An economics professor and his student are walking down the Champs-Élysées. The student spots a hundred franc note on the sidewalk. The starved student excitedly bends over to grab it, when the professor suddenly taps him back with his cane, wags his finger, and says <<Don’t bother, it’s an illusion, for the note can’t exist … for if it did, somebody would have picked it up by now.>>
It’s funny to think about, but, what if they were two agents?
Never miss a single issue
Subscribe now to get the gatodo newsletter delivered straight to your inbox
